

Surgery for chronic exertional compartment syndrome of the leg produces excellent results in the anterior and lateral compartments, and less predictable results when the posterior compartments are involved. Also, this surgery is typically an elective procedure - not an emergency.
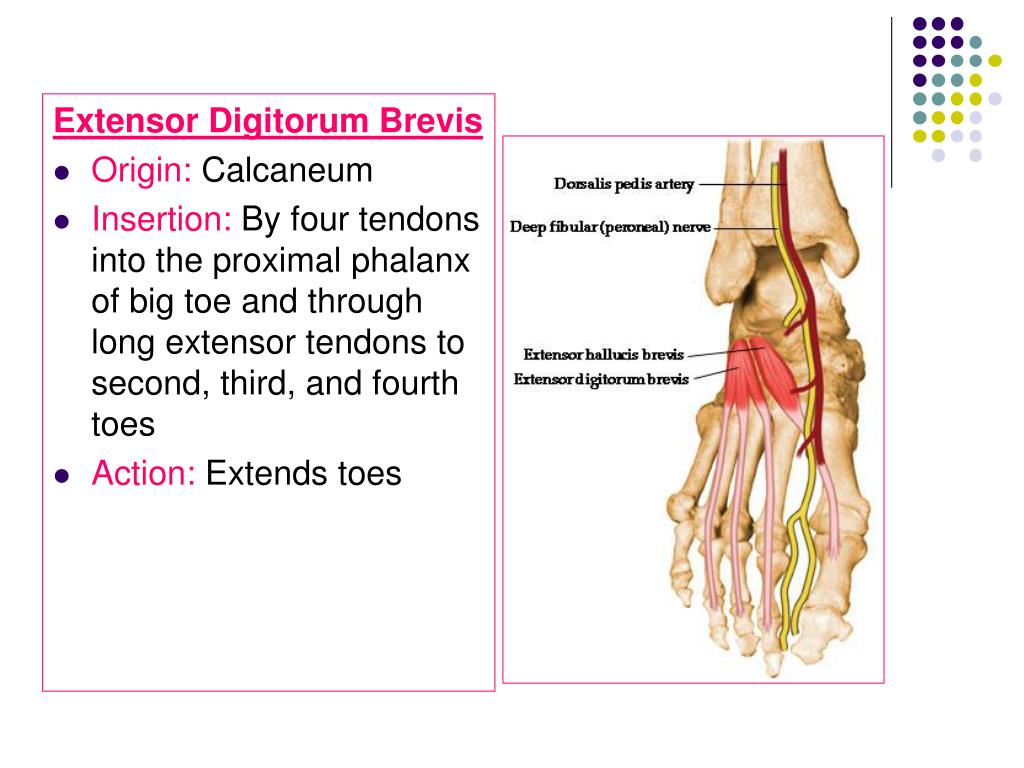
FASCIAL COMPARTMENTS OF LEG SKIN
Usually, the skin incision for chronic compartment syndrome is shorter than the incision for acute compartment syndrome. Similar to the surgery for acute compartment syndrome, the operation is designed to open the fascia so there is more room for the muscles to swell. If conservative measures fail, surgery may be an option. Changing from heel strike to toe running may modify symptoms depending on the compartments involved.Symptoms may be relieved by switching surfaces. Some athletes have symptoms that are worse on certain surfaces (concrete vs.Cross-training with low-impact activities may be an option.Your symptoms may subside if you avoid the activity that caused the condition.
FASCIAL COMPARTMENTS OF LEG FULL
Physical therapy, orthotics (inserts for shoes), and anti-inflammatory medicines may be of limited benefit in relieving symptoms and generally do not allow return to full activity. Chronic (Exertional) Compartment Syndrome The incision is repaired later when swelling subsides. Sometimes, the swelling is severe enough that the skin incision cannot be closed immediately. Your doctor will make an incision and cut open the skin and fascia covering the affected compartment. There is no effective nonsurgical treatment. SymptomsĪcute compartment syndrome is a surgical emergency. This is usually relieved by discontinuing the exercise, and is usually not dangerous. People who participate in activities with repetitive motions, such as running or marching, are more likely to develop chronic compartment syndrome. The pain and swelling of chronic compartment syndrome is caused by exercise. If you have a cast, contact your doctor immediately.Ĭhronic (Exertional) Compartment Syndrome If symptoms of compartment syndrome develop, remove or loosen any constricting bandages. Casts and tight bandages may lead to compartment syndrome. Taking steroids is a possible factor in compartment syndrome. This can happen after severe intoxication with alcohol or other drugs.
The development of compartment syndrome in this manner usually occurs in people whose brain function is impaired. Most healthy people will naturally move when blood flow to a limb is blocked during sleep.

Lying for too long in a position that blocks a blood vessel, then moving or waking up can cause this condition. A blood vessel can also be blocked during sleep. This may occur after a surgeon repairs a damaged blood vessel that has been blocked for several hours. Reestablished blood flow after blocked circulation.It can also happen after overly vigorous exercise that causes muscle tissue to break down (rhabdomyolysis) This type of injury can occur when a motorcycle falls on the leg of the rider, or a football player is hit in the leg by another player's helmet. Rarely, it develops after a relatively minor injury.Ĭonditions that may bring on acute compartment syndrome include: Knowledge of variations of the SFN with reference to compartmental anatomy of the leg may be useful in fascial release operations.Acute compartment syndrome usually develops after a severe injury, such as a car accident or a broken bone. In the remaining 5.3% of the specimens the SFN had branches both in the anterior and lateral compartments (Type III). In 23.7%, the SFN penetrated the anterior intermuscular septum, 12.7 cm inferior to the apex of the head of fibula and coursed in the anterior compartment (Type II). In 71% of the cases, the SFN coursed entirely within the lateral compartment of the leg (Type I). Three particular types in the course of SFN were determined. Thirty-eight legs of 20 cadavers fixed in 10% formaldehyde were dissected and the compartmental anatomy of the SFN investigated. The aim of this study was to investigate the localization of the superficial fibular nerve (SFN) in the lateral and the anterior compartments. Incompletely released fascial compartments, soft tissue damage, and neurovascular injury, which includes superficial fibular nerve injury are common complications. Fasciotomy can be performed either with classical open or minimally invasive techniques including endoscopically assisted or semi blind subcutaneous releases. Fasciotomy is currently the mainstay for surgical treatment. Compartment syndrome is a common cause of lower extremity pain via an increased intra-compartmental pressure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
